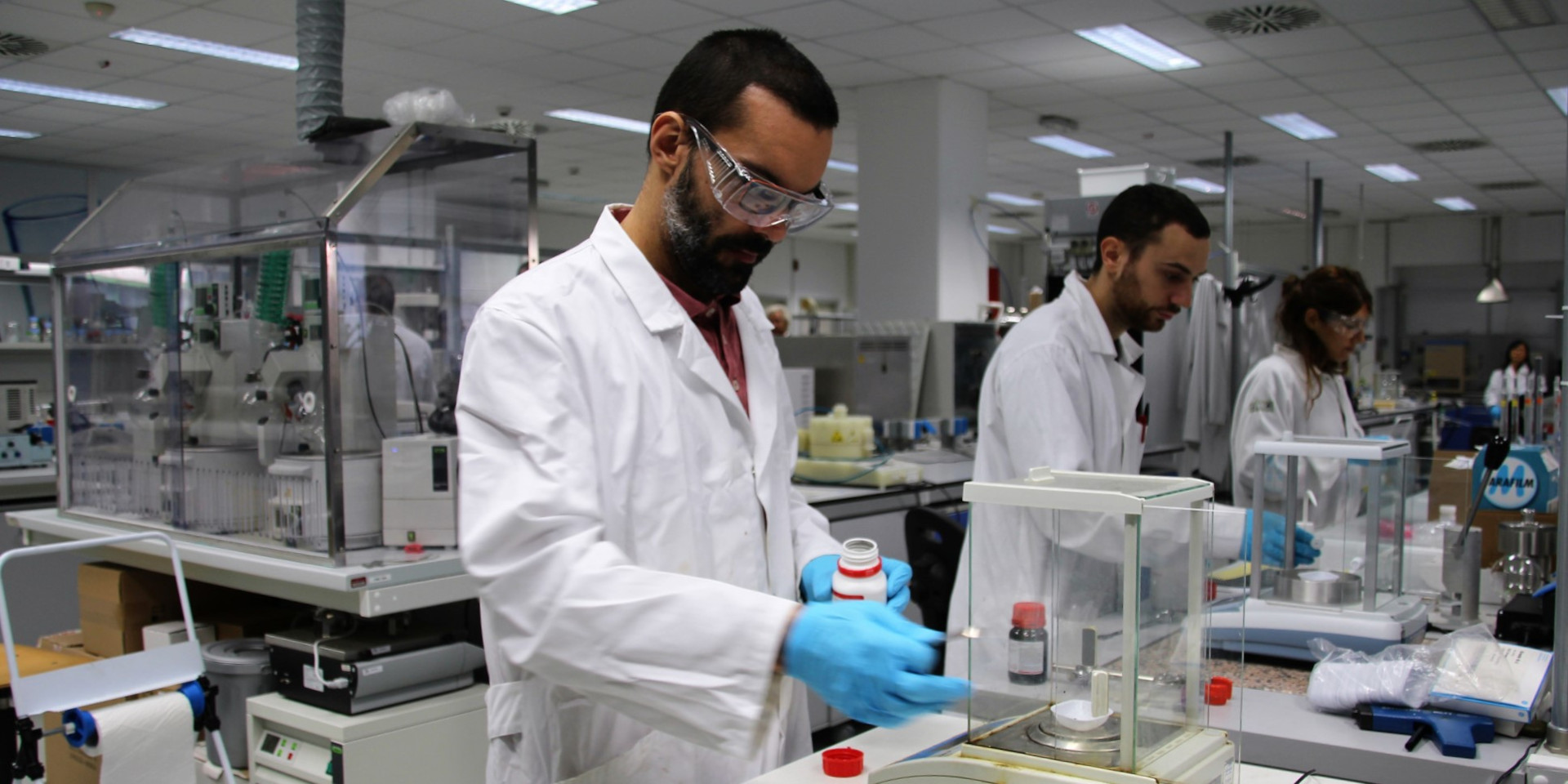
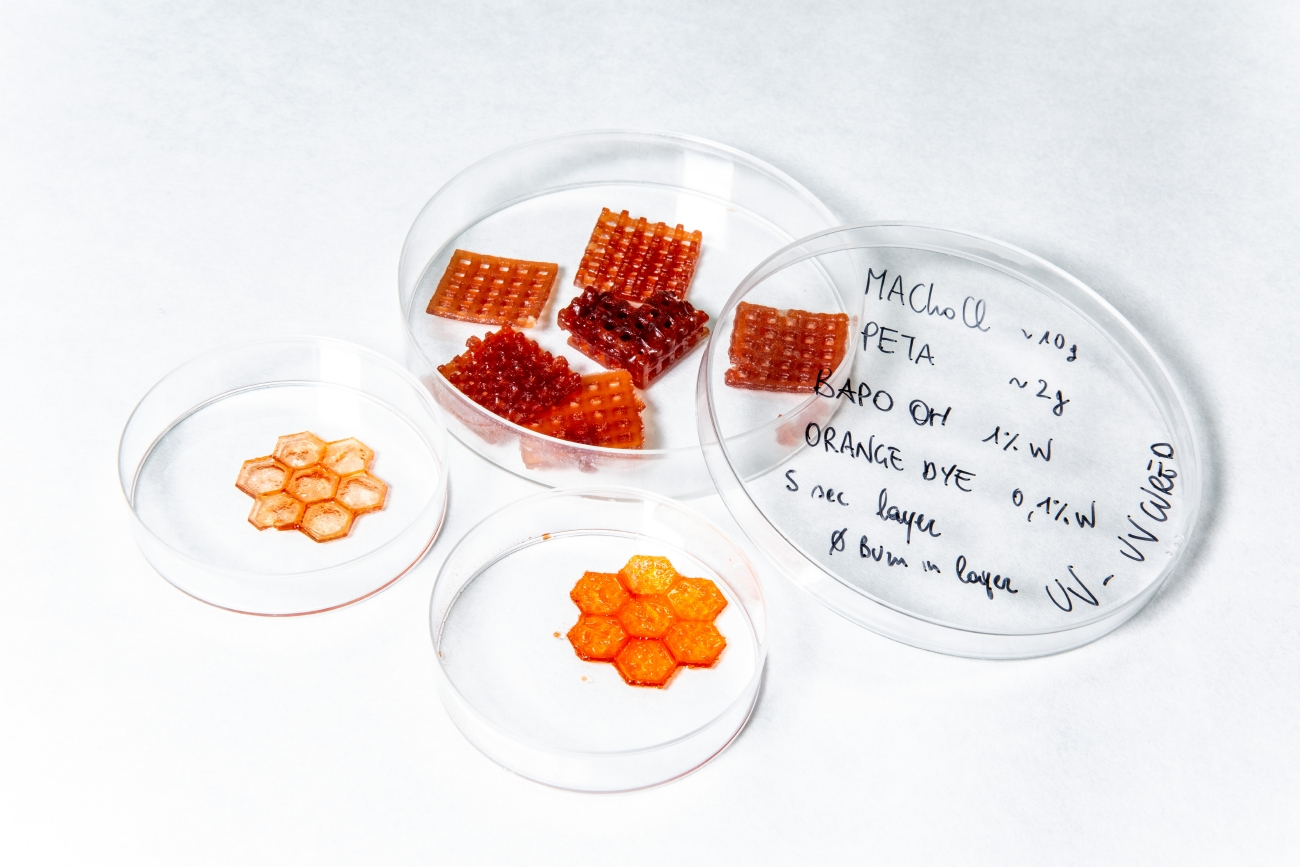
Seeking solutions from the microbial world
We use microbial cultures for various purposes: we valorize CO2 and industrial liquid waste streams by transforming it into useful products through acetogenic bacteria and microalgae; we recover critical metals from industrial wastewater and electronic waste using methanogenic archaeal strains; we produce biohydrogen through anaerobic dark fermentation; we study underground hydrogen storage by analyzing microbial activity in depleted reservoirs.